Oxygen levels in the atmosphere during the mid-Proterozoic — about 1.4 billion years ago — were higher than previously thought, according to an international team of researchers who looked at oxygen combined with sulfur to determine that previous numbers were probably lower limits, not maximums.
Demi Badejo is an epidemiologist for the Maryland Department of Health and a 2019 graduate from Penn State. While she was a health policy and administration major at University Park, she decided to enroll in City Semester — an urban sustainability program offered through the Penn State Center Pittsburgh, in collaboration with the Sustainability Institute at Penn State. Badejo said the experience taught her more than urban sustainability; it changed her career path.
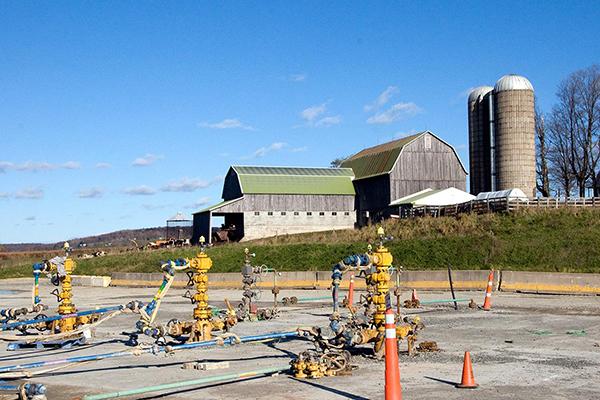
Unconventional oil and gas development (UOGD), commonly known as fracking, has helped Pennsylvania retain its status as a leading energy exporter, but UOGD processes come with a host of environmental and public health concerns. A new grant from HEI Energy will allow researchers to explore possible links between fracking and water contaminants in southwestern Pennsylvania.
Susan L. Brantley, Barnes Professor of Geosciences and director of the Earth and Environmental Systems Institute at Penn State, was elected a foreign associate of the French Academy of Sciences. The honor recognizes Brantley for her distinguished contributions to the field of earth sciences.
When Cameron Brown was born, his mother — a labor and delivery nurse at a hospital in Queens, New York — introduced him to a tradition she gleaned from a Nigerian mother who was once her patient. As Brown took his first breaths, she whispered in his ear what she believed he would become: an architect.
Ancient rocks on the coast of Oman that were once driven deep down toward Earth’s mantle may reveal new insights into subduction, an important tectonic process that fuels volcanoes and creates continents, according to an international team of scientists.
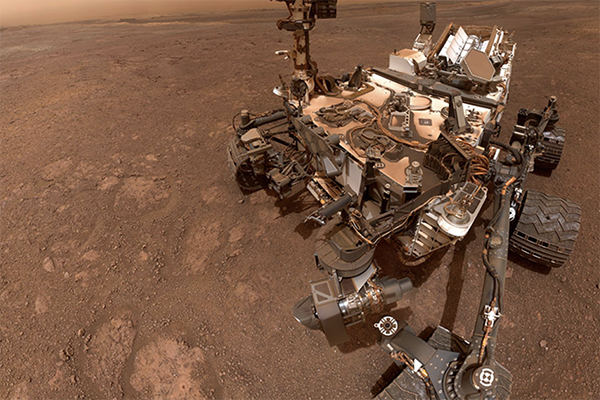
NASA's Curiosity rover landed on Mars on Aug. 6, 2012, and since then has roamed Gale Crater taking samples and sending the results back home for researchers to interpret. Analysis of carbon isotopes in sediment samples taken from half a dozen exposed locations, including an exposed cliff, leave researchers with three plausible explanations for the carbon's origin — cosmic dust, ultraviolet degradation of carbon dioxide, or ultraviolet degradation of biologically produced methane.
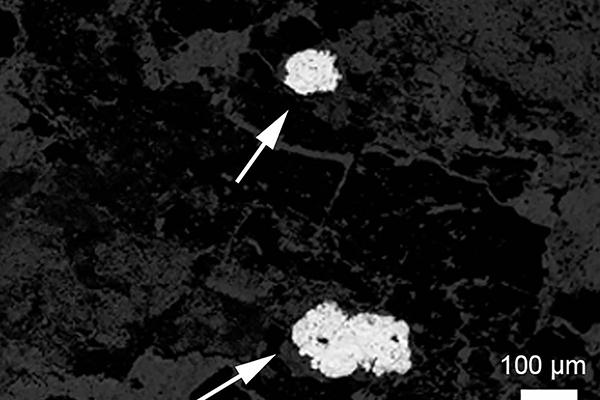
When one organism’s trash contains traces of human treasure, look for ancient microbial activity, according to researchers who found elemental silver in fossilized worm dung.
When Judit Gonzalez-Santana conducts her research, she first looks to space. With each passing of radar satellites in the Earth’s orbit, changes in elevation of the ground at Guatemala’s Pacaya Volcano are recorded, providing data to the Penn State doctoral candidate in geosciences, who is training to become a volcanologist.
Switching from coal to natural gas in power plants can reduce how much sulfur dioxide, a gas that smells like a freshly struck match, is emitted into the atmosphere and ultimately how much sulfate pollution enters waterways, according to a Penn State-led research team that has developed a model to detect if the recent switch from coal to gas is affecting streams.